Ignition coil
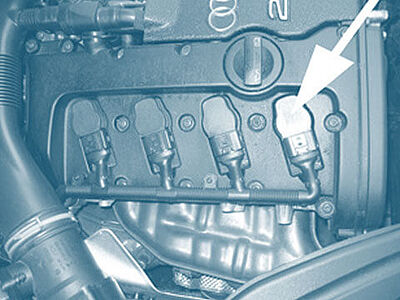
The ignition coil must transform the relatively low 12 V on-board vehicle voltage to the high ignition voltage required and supply the energy stored in that voltage to the spark plug. The functional principle...
Depreciation
Ignition coils are exposed to permanent mechanical and thermal stress. Their condition and function is checked as part of regular inspection and maintenance in a garage so that damage can be detected at an early stage and failure prevented.
Safety
According to annual breakdown figures collated by the ADAC, faults affecting the electrics and the ignition system continue to top the list, making up for more than half of all recorded breakdowns. On account of the continued rise in the number of electronic components and their networking via bus systems, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) has gained significantly in importance in recent years.
As as result, every electronic component must meet the following requirements:
- It must be resistant to external influencing factors under all specific operating conditions.
- It must not interfere with other electrical systems.
- During operation, it must support error-free radio reception both inside the vehicle and in the immediate surroundings.
Function

The ignition coil must transform the relatively low 12 V on-board vehicle voltage to the high ignition voltage required and supply the energy stored in that voltage to the spark plug. The functional principle of the ignition coil is relatively simple. It has a primary winding (small number of turns) and a secondary winding (lots of turns). The turn ratio between the number of primary and secondary winding turns determines the level of the voltage generated at the output. When on-board voltage is connected to the primary winding of the ignition coil, a current flows through the primary winding, generating a magnetic field in the ignition coil.
Interrupting the current flow in the primary winding takes away the magnetic field suddenly, simultaneously generating the high voltage required for ignition sparking in the secondary winding. How the high voltage generated by the ignition coil is transferred to the spark plug will vary depending on the ignition system, the vehicle generation and the vehicle model. In older vehicles, a mechanical ignition distributor distributes the high voltage to the spark plugs. The ignition distributor was replaced when fully electronic ignition with direct connection between ignition coil and spark plug was introduced.
Environmental protection
An ignition system that is in perfect working order provides the basis for the correct and proper operation of the catalytic converter. It reduces pollutant emissions, thereby playing an active part in the protection of the environment. However, the catalytic converter is sensitive to mechanical stress and strain, overheating and control errors. Exposure to excess stress and strain of this nature can impair its performance or even cause it to fail completely. As a result, pollutant emissions would increase tenfold.
Downloads
Here you can find all available downloads for the topic "Ignition coil":
All file downloads:












