Binary lambda sensor
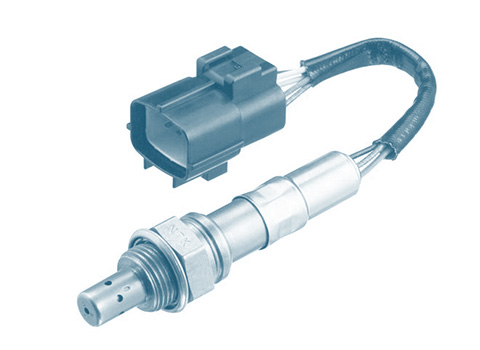
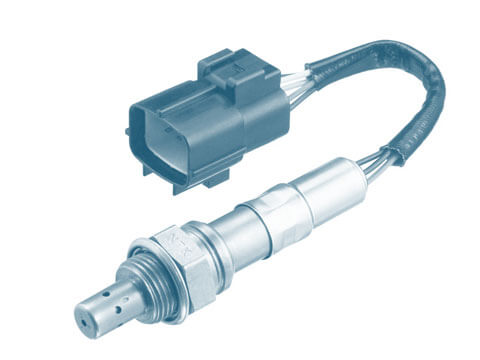
A lambda sensor is an oxygen concentration sensor which measures the differences in oxygen content between the exhaust gas and the ambient air to ensure the optimum mixture composition. One type of lambda sensor is the binary lambda sensor.
Function
A lambda sensor measures the residual oxygen content of the exhaust gas. It emits a voltage signal based on the residual oxygen contained in the exhaust gas.  The engine control unit uses this voltage signal to determine the current mixture composition. With binary lambda sensors, the sensor signal switches back and forth between two values. Depending on the composition, the quantity of fuel injected is reduced (rich mixture) or increased (lean mixture).
The engine control unit uses this voltage signal to determine the current mixture composition. With binary lambda sensors, the sensor signal switches back and forth between two values. Depending on the composition, the quantity of fuel injected is reduced (rich mixture) or increased (lean mixture).
Types of binary lambda sensor
A basic distinction is made between two types of binary lambda sensor: Zirconium dioxide and titanium dioxide. The zirconium dioxide lambda sensor is the most widely used type. Mode of operation of zirconium dioxide binary sensor The zirconium dioxide sensor element is finger-shaped and hollow. The inner side is in contact with the ambient air, the outer side is in the exhaust gas flow. Both sides are coated with a thin porous platinum layer which acts as an electrode. When the zirconium dioxide binary sensor reaches its operating temperature, oxygen ions start to flow on account of the difference in oxygen concentration. Oxygen ions move from the reference side in the direction of the exhaust gas to balance this out. On account of the resultant difference in potential (voltage between two electrically charged bodies), a voltage is applied to the platinum electrodes. The sensor signal is roughly 0.1 V for a lean mixture and 0.9 V for a rich mixture. Mode of operation of titanium dioxide binary sensor In contrast to zirconium dioxide binary sensors, titanium dioxide binary sensors do not actually produce any voltage. Instead, their resistance changes in line with the residual oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. Titanium dioxide binary sensors do not need any reference air. The titanium dioxide is less conductive with a high oxygen content (lambda greater than 1) and more conductive with a low oxygen content (lambda less than 1). If a voltage is applied to the element, the output voltage changes in accordance with the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. The operating temperature of these lambda sensors is 700°C. A titanium dioxide binary sensor is usually more compact than the zirconium dioxide version as it does not require any ambient air as reference.
Environmental protection
Lambda sensors are indispensable for the efficient conversion of exhaust gases. More modern vehicles often employ two lambda sensors. Lambda sensors are subject to extreme loads. A properly functioning lambda sensor is a prerequisite for reliable engine operation and thus for the following three factors:
- Low fuel consumption
- Low pollutant emissions
- Correct emission values